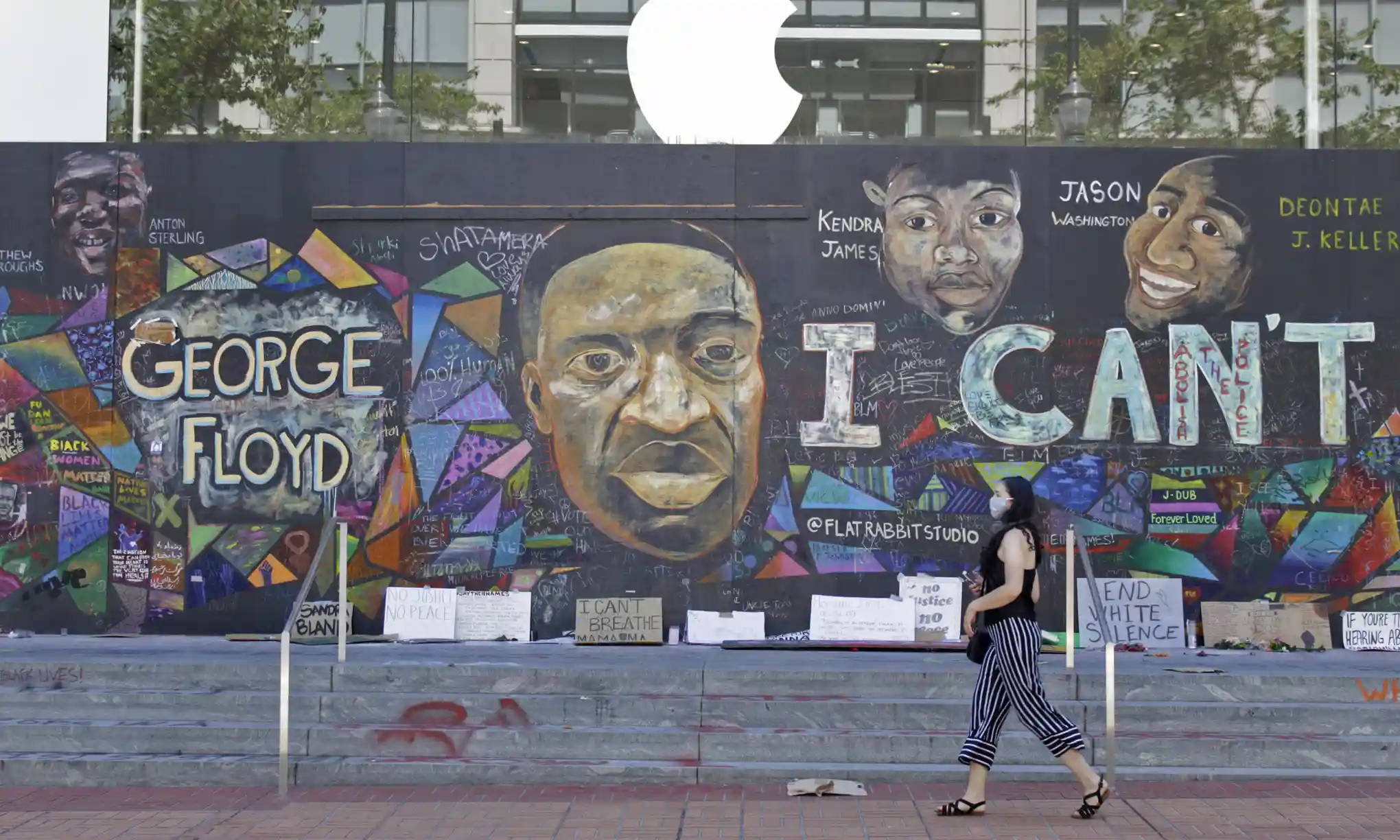
As Joe Biden pushes to ‘fund the police’, data from Mapping Police Violence shows high rates of deaths at the hands of law enforcement persist
Police officers in America continue to kill people at an alarming rate, according to a data analysis that has raised concerns about the Biden administration’s push to expand police investments amid growing concerns about crime.
Law enforcement in the US have killed 249 people this year as of 24 March, averaging about three deaths a day and mirroring the deadly force trends of recent years, according to Mapping Police Violence, a non-profit research group. The data, experts say, suggests in the nearly two years since George Floyd’s murder, the US has made little progress in preventing deaths at the hands of law enforcement, and that the 2020 promises of systemic reforms have fallen short.
Police have killed roughly 1,100 people each year since 2013. In 2021, officers killed 1,136 people – one of the deadliest years on record, Mapping Police Violence reported. The organization tracks deaths recorded by police, governments and the media, including cases where people were fatally shot, beaten, restrained, and Tasered. The Washington Post has reported similar trends, and found that 2021 broke the record for fatal shootings by officers since the newspaper started its database tracking in 2015.
“The shocking regularity of killings suggests that nothing substantive has really changed to disrupt the nationwide dynamic of police violence,” said Samuel Sinyangwe, a data scientist and policy analyst who founded Mapping Police Violence and Police Scorecard, which evaluates departments. “It demonstrates that we’re not doing enough, and if anything, it appears to be getting slightly worse year over year.”
Advocates argue that the persistent rate of killings was a critical reason the US should not be expanding its police forces.
Joe Biden, who has repeatedly said to “fund the police”, released a budget proposal earlier this week for $30bn in law enforcement and crime prevention efforts, including funding to put “more police officers on the beat”. The proposal, which called for the expansion of “accountable, community policing”, sparked immediate criticisms from racial justice groups. The Movement for Black Lives noted that the White House was proposing only $367m to support police reform and said Biden’s budget “shows a blatant disregard for his promises to Black people, masked as an effort to decrease crime”.
Michael Gwin, a White House spokesperson, said in an email that Biden had been “consistent in his opposition to defunding the police and in his support for additional funding for community policing”, and “remains committed to advancing long-overdue police reforms”.
“The president, along with the overwhelming majority of Americans, knows that we can and must have a criminal justice system that both protects public safety and upholds our founding ideals of equal treatment under the law. In fact, those two goals go hand-in-hand. That approach is at the core of the president’s comprehensive plan to combat crime by getting guns off the streets, and by investing in community-oriented policing and proven community anti-violence programs,” he added.

During the national uprisings after Floyd’s murder, “defund the police” became a central rallying cry, with advocates arguing reform efforts had failed to prevent killings and misconduct. Cities could save lives by reducing police budgets, limiting potentially deadly encounters with civilians, and reinvesting funds into community programs that address root causes of crime, activists have said.
Some cities initially responded with modest cuts to police budgets, in some cases removing officers from schools, traffic enforcement and other divisions, and investing in alternatives. But over the last year, an uptick in gun violence and homicides has prompted a backlash to the idea of defunding (even as the current crime rate remains significantly lower than decades prior). With intense media coverage of crime, officials have been pressured to abandon reforms, prioritize harsh punishments and invest more in police. Cities that made small cuts have largely restored and expanded law enforcement budgets.
“To invest more into a system that we all know is broken is really a slap in the face to everyone who marched in summer 2020,” said Chris Harris, director of policy at the Austin Justice Coalition in Texas. “It reflects just a real lack of solutions to the problems that we face. It’s just more of the same – even if it’s exactly the thing that we know continues to hurt and kill people.”
Harris said it was disappointing to see calls for police expansion at the federal level, given the George Floyd Act, the national reform measure proposed after the protests, did not succeed. He said he was not surprised that the killings by police continue apace: “We fail to deal with the underlying issues that often drive police interactions in our communities, partly because we’re funding this law enforcement response rather than the upfront supports and services that could help people.”
Gwin noted that the White House was exploring possible executive action to pass reforms after Republicans blocked negotiations over legislation.
Sinyangwe pointed to a data analysis in Los Angeles, which showed that in recent years, one-third of incidents in which Los Angeles police department (LAPD) officers used force involved an unhoused person: “Instead of using force against homeless people, we should be investing in services and creating unarmed civilian responses to these issues.”
But in LA, where housing and outreach efforts have fallen short, there has been an escalating law enforcement crackdown on street encampments. And LAPD is on track to get a large budget boost, despite a sharp increase in killings by officers in 2021.
Proponents of police budget increases argue that law enforcement is the solution to violence, but Sinyangwe noted that fewer than 5% of arrestsnationally are for serious violent crimes. And research has shown that when police forces expand, there are more arrests for low-level offenses, he said. And many high-profile killings by police have involved stops for alleged low-level crimes.

Kaitlyn Dey, an organizer in Portland, Oregon, said it was frustrating to see officials push a narrative that cities need to “re-fund the police” when municipalities have largely failed to defund law enforcement in the first place.
“We have to start chipping away at how many officers there are, what kind of equipment they have – that is going to reduce [police] violence, because they’re not going to be able to enact it if you take away their resources,” she said.
There are documented solutions that could reduce killings, said Alex S Vitale, sociology professor at Brooklyn College and an expert on policing. He noted estimates suggesting that 25% to 50% of people killed by police were having a mental health crisis.
“If we would develop non-police mental health crisis teams, and improve community-based mental health services, we could save hundreds of lives a year,” he said.
Vitale, author of The End of Policing, pointed to a program in Denver that sends mental health clinicians and paramedics to respond to certain 911 calls, which is now dramatically expanding after a successful pilot. Health experts have responded to thousands of emergency calls since 2020, and have never had to call police for backup, the Denver Post reported.
“While the media has mobilized crime panics to try and shut down talk of reducing our reliance on policing, organizations across the country are doing grassroots work in communities to demand these alternatives,” he said.