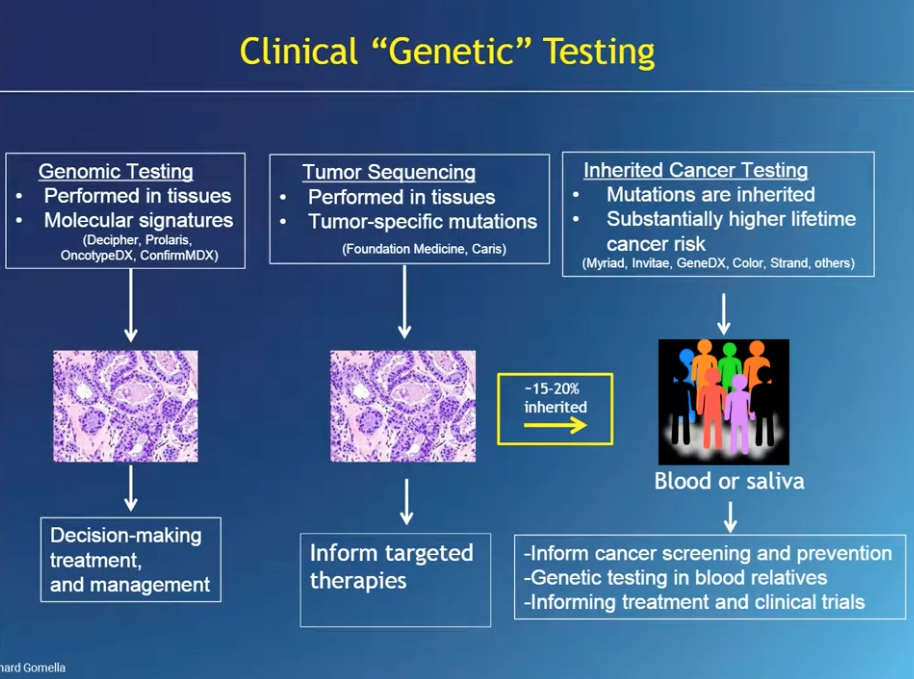
A recent study published in JAMA Network Open has found that genetic profiling can help identify individuals at an increased risk of dying from prostate cancer. By measuring the polygenic risk score (PRS), researchers were able to pinpoint gene variants that could potentially lead to prostate cancer or death from the disease. According to the study, men in the top 10% of PRS have a 40-50% chance of developing prostate cancer in their lifetime.
The study, which followed almost 20,000 participants in the U.S. and Sweden over a 20-year period, found that both genetic and lifestyle factors play a role in increasing the risk of death from prostate cancer. Individuals with a high PRS were at a 3-fold increased risk of early death from prostate cancer and a 2-fold increased risk of late death. The study also revealed that lifestyle factors seemed to be more important for individuals with a higher genetic risk.
Health experts, including radiation oncologist Trevor Royce and urologic surgeon Jeffrey Yoshida, emphasize the importance of lifestyle modifications in reducing the risk of prostate cancer. By adopting healthy habits such as maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking, individuals can potentially lower their risk of developing the disease.
While the study highlights the potential benefits of genetic testing in identifying high-risk individuals, some experts caution that more research is needed to validate these findings. Medical oncologist Przemyslaw Twardowski acknowledges the importance of addressing modifiable lifestyle factors but notes that further studies are required to confirm the impact of lifestyle changes on reducing the risk of developing fatal prostate cancer.
Overall, the study suggests that early detection and lifestyle interventions may play a crucial role in reducing the number of early deaths from prostate cancer. By engaging in conversations with healthcare providers and undergoing recommended screenings, individuals can take proactive steps towards better prostate health and potentially reduce their risk of mortality from the disease.
Source: https://www.pressrundown.com/health/genetic-tests-identify-prostate-cancer-risk-for-early-detection