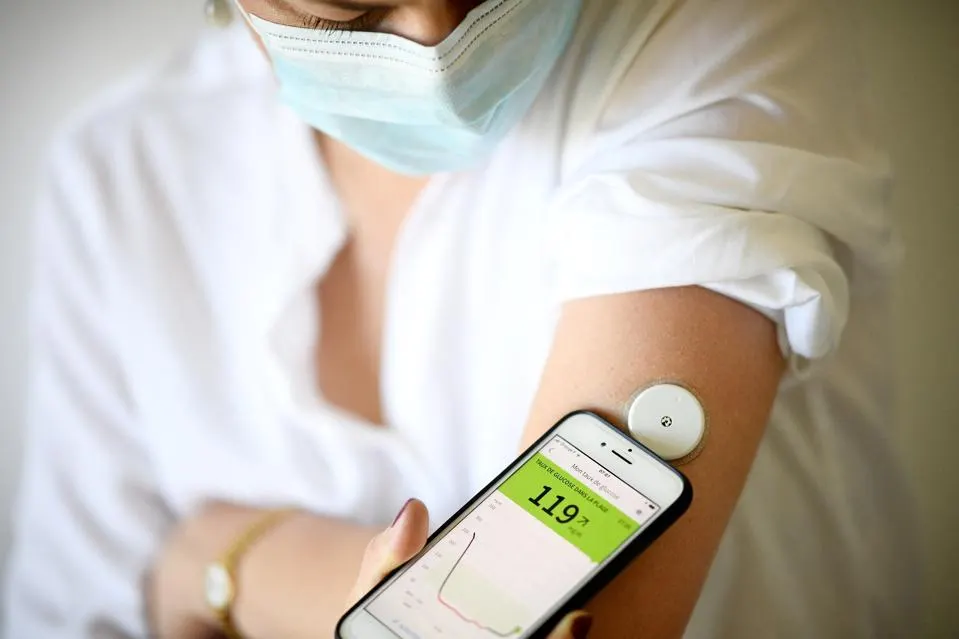
A recent study published in The Lancet has revealed that the global prevalence of diabetes has more than doubled in the last three decades, with over 800 million individuals now living with the disease. This represents a significant increase of 630 million individuals since 1990, with 14% of the global population now affected by diabetes. The majority of cases are concentrated in four countries, with India having the highest number of cases, followed by China, the United States, and Pakistan.
The study also highlighted the growing disparities in the treatment of diabetes, with more than half of diabetics aged 30 and over not receiving the necessary treatment in 2022. Treatment coverage was found to be lowest in middle and low-income countries, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa and south Asia.
Diabetes can have serious health consequences, including heart disease, kidney failure, and vision loss. It is the eighth leading cause of death globally and the number one cause of kidney failure, lower leg amputations, and adult blindness in America.
In order to address the global burden of diabetes, major systemic changes are needed. This includes implementing health policies that promote healthy lifestyles, increasing access to healthcare, and investing in preventive measures. Universal healthcare insurance and infrastructure that supports preventive doctor visits are crucial in ensuring that individuals receive the necessary treatment for diabetes.
Furthermore, tackling the obesity epidemic is essential in preventing type II diabetes, as obesity is a major risk factor for the disease. Providing access to healthier food options and promoting physical activity in underserved communities can help reduce the burden of diabetes globally.
Overall, the study underscores the urgent need for action to address the growing prevalence of diabetes and ensure that individuals receive the necessary treatment to prevent serious complications. By taking a proactive approach and implementing comprehensive strategies, we can work towards a healthier global environment and reduce the impact of diabetes on millions of individuals worldwide.