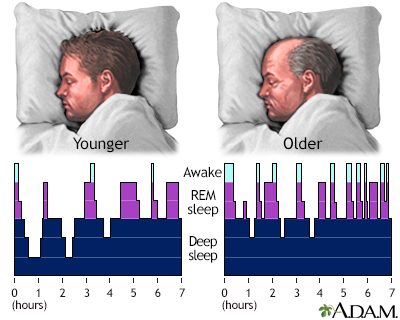
As we age, our sleeping patterns often change, with shifts in circadian rhythms and fluctuations in sleep cycles becoming more common. According to a fact sheet from the National Council on Aging, factors such as decreased production of growth hormone and melatonin, as well as changes in the brain’s sleep/wake cycle, can contribute to interrupted sleep in older adults. These changes may result in taking longer to fall asleep, staying awake at night, or waking up too early.
Despite these changes, it is crucial for adults of all ages to prioritize getting a healthy amount of sleep, ideally between seven and nine hours per night. Practicing good sleep hygiene, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and addressing root causes of sleep issues, can help improve sleep quality and continuity.
Lifestyle habits also play a significant role in sleep quality, with factors like stress, mental health issues, diet, exercise, and substance use impacting our ability to get a good night’s rest. Addressing lifestyle factors, such as managing stress, maintaining a balanced diet, and limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, can contribute to better sleep.
Additionally, medications can also affect sleep quality, with certain medications like diuretics, antidepressants, and cold medications potentially interfering with sleep. Polypharmacy, or the regular use of multiple medications, can further complicate sleep patterns in older adults. It is important to discuss any medications and their potential interactions with a healthcare provider to optimize sleep quality.
Overall, understanding the impact of age-related changes, lifestyle habits, and medications on sleep quality is crucial for maintaining good sleep health as we age. By addressing these factors and seeking professional guidance when necessary, older adults can work towards improving their sleep and overall well-being.
Source: https://www.pressrundown.com/health/how-aging-affects-sleep?lctg=6508b820e8179a307e601d89