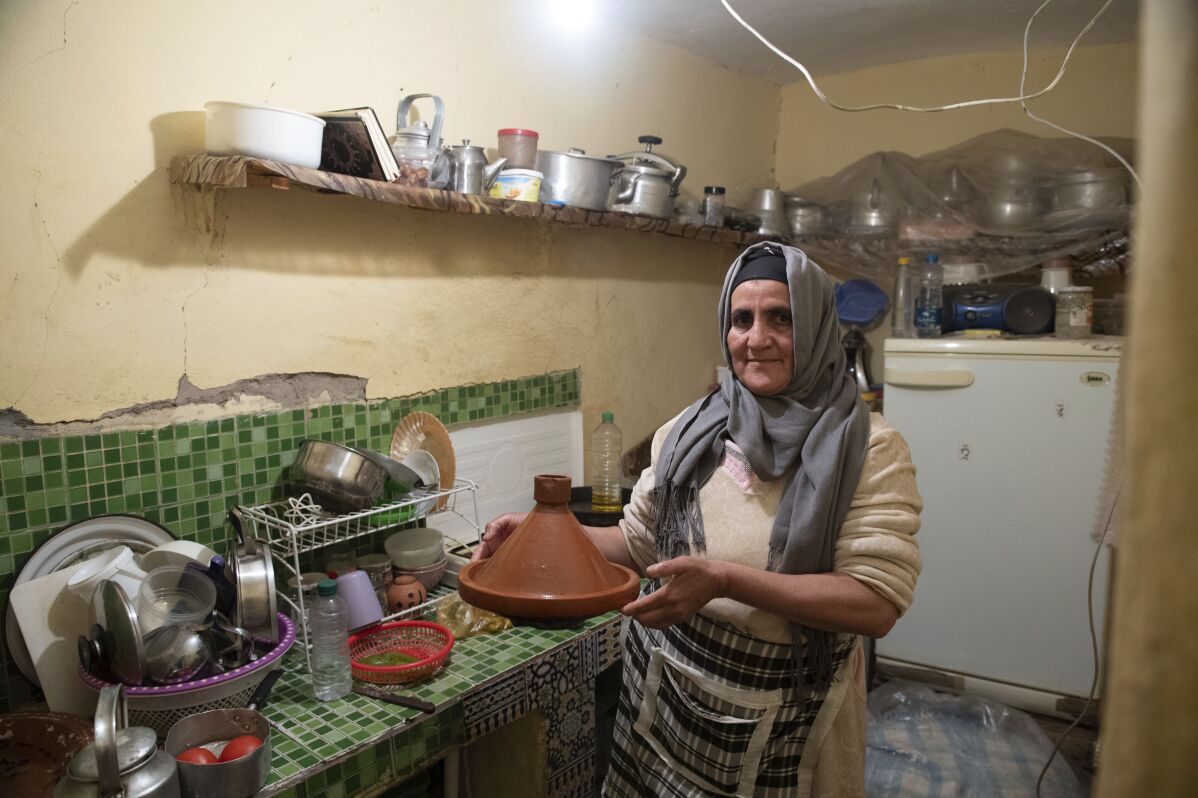
AMIZMIZ, Morocco (AP) — An earthquake months ago left parts of her home cracked and crumbling, but Fatima Barri felt wrong spending Islam’s holy month of Ramadan in a tent.
Thankful to be spared by the 6.8-magnitude quake that killed thousands around her in Morocco’s Atlas Mountains, she stood in her damaged house and cooked the traditional meals to break the daily fasts. It felt safe enough, she said, until a 3.3-magnitude tremor rumbled through two weeks ago.
She was terrified, but stayed.
“It’s my house. I have nowhere else to go,” the 57-year-old mother of three said and shrugged.
Like many of her neighbors, she’s tired of waiting for normal life to resume. For months after the quake killed nearly 3,000 Moroccans in September, Barri stayed in a hot and stuffy government-provided tent.
For Ramadan, she and others honored their traditions amid the rubble, cooking tagine in clay pots and making bread and tea on their stoves. On Wednesday, as Eid al-Fitr began, the holiday mood for many Moroccans vacillated between festiveness and despair.
During the month of reflection, Barri appreciated the family and community gatherings as well as small pleasures like the mint and verbena she replanted in buckets near the debris on her roof.
Her community of Amizmiz is one of the larger towns shaken by the earthquake. Many people who had promised to stay and rebuild such communities have since moved to larger cities.
For Morocco, the task of rebuilding is daunting. The government estimates that more than 300,000 people were affected by the earthquake in Marrakech and the five hardest hit mountain provinces, where more than 4.2 million reside. There are plans to rebuild schools, roads and hospitals and help farmers who lost their herds.
The government has said it is committed to returning people to their homes and hopes the reconstruction will bring new development opportunities to a region that has long lacked the infrastructure of Morocco’s tourist hubs and coastal cities.
But on the ground, there is frustration.
Construction crews working to restore multi-story buildings for community associations are angry that they haven’t received more guidance from the government on how to build for future quakes. Untrained, they are stacking cinderblocks and plaster on the ruins of multi-story buildings.
A month after the disaster, protesters angry at local authorities and suspicious of corruption marched through the town demanding the promised government aid.
At the end of January, a government rebuilding commission said nearly 58,000 families had received monthly stipends of 2,500 dirhams — or $250 — and more than 20,000 households had received an initial installment of reconstruction assistance.
The assistance was announced in September, but after reported distribution problems, the Interior Ministry opened a register for residents to request it 2 1/2 months later.
In total, officials have said rebuilding will cost 120 billion dirhams ($12 billion) and take about five years. International aid has been offered, including a $1.3 billion loan from the International Monetary Fund.
In Amizmiz, there are signs of resilience, economic activity, and life returning to normal. There are also signs that the road to recovery will be long. Vendors sell honey, flour and sprinkles used to bake Ramadan sweets; men watch Turkish soap operas on televisions; women displaced from their homes wash clothes in community fountains.
In plastic tents — which magnify the sun’s heat — some residents said they were surviving on the monthly stipends and waiting on a larger sum promised for reconstruction. Many told The Associated Press they had received nothing at all.
Last month, the Moroccan Institute for Policy Analysis published survey data taken from October to December in which only 11% of people directly affected by the earthquake said they had received support from the government.
The most difficult to reach areas have faced more challenges.
In some villages, the government has used sheet metal and concrete to build barracks-style temporary homes. In Amizmiz there are only tents.
The community is proud of coming together to help one another. A community association, Alyatim, hosted nightly dinners serving up to 250 people breaking their Ramadan fasts.
“The help only comes from the associations. No help comes from the government,” said Abdelaziz Smina, a 50-year-old blacksmith.
Smina said local authorities told him that his cracked concrete home — currently held upright by wooden stilts — wasn’t damaged enough to qualify for aid. His neighbors have yet to receive assistance funds to allow them to buy metal doors from him for their own rebuilding.
But Smina and his family have seen Ramadan as a chance to reaffirm their faith in the face of disaster.
“It’s all up to God,” he said.