Leprosy, once a disease confined to history books, is experiencing an unexpected resurgence in the United States, particularly in Florida. With 159 cases reported in 2020 alone, this ancient disease’s modern manifestation has become a pressing public health concern. This post aims to explore the resurgence of leprosy, delve into the new cases, and discuss the public health response, shedding light on what this means for society today.
The Resurgence Of Leprosy In The U.S.

The resurgence of leprosy in the U.S. is a complex phenomenon that has been gradually building since the 1980s. After a significant reduction in cases through 2000, recent reports demonstrate a gradual increase, with states like Florida, California, and Texas becoming hotspots. This trend raises questions about the factors contributing to the rise and the implications for public health.
In 2020, Central Florida accounted for nearly one-fifth of reported cases in the country, making it a focal point for understanding this resurgence. The statistics reveal a pattern that requires careful examination, not only of the disease itself but also of the broader social and environmental factors. This leads to the need to take a closer look at the nature of leprosy, its symptoms, and its causes.
Understanding Leprosy: Causes And Symptoms

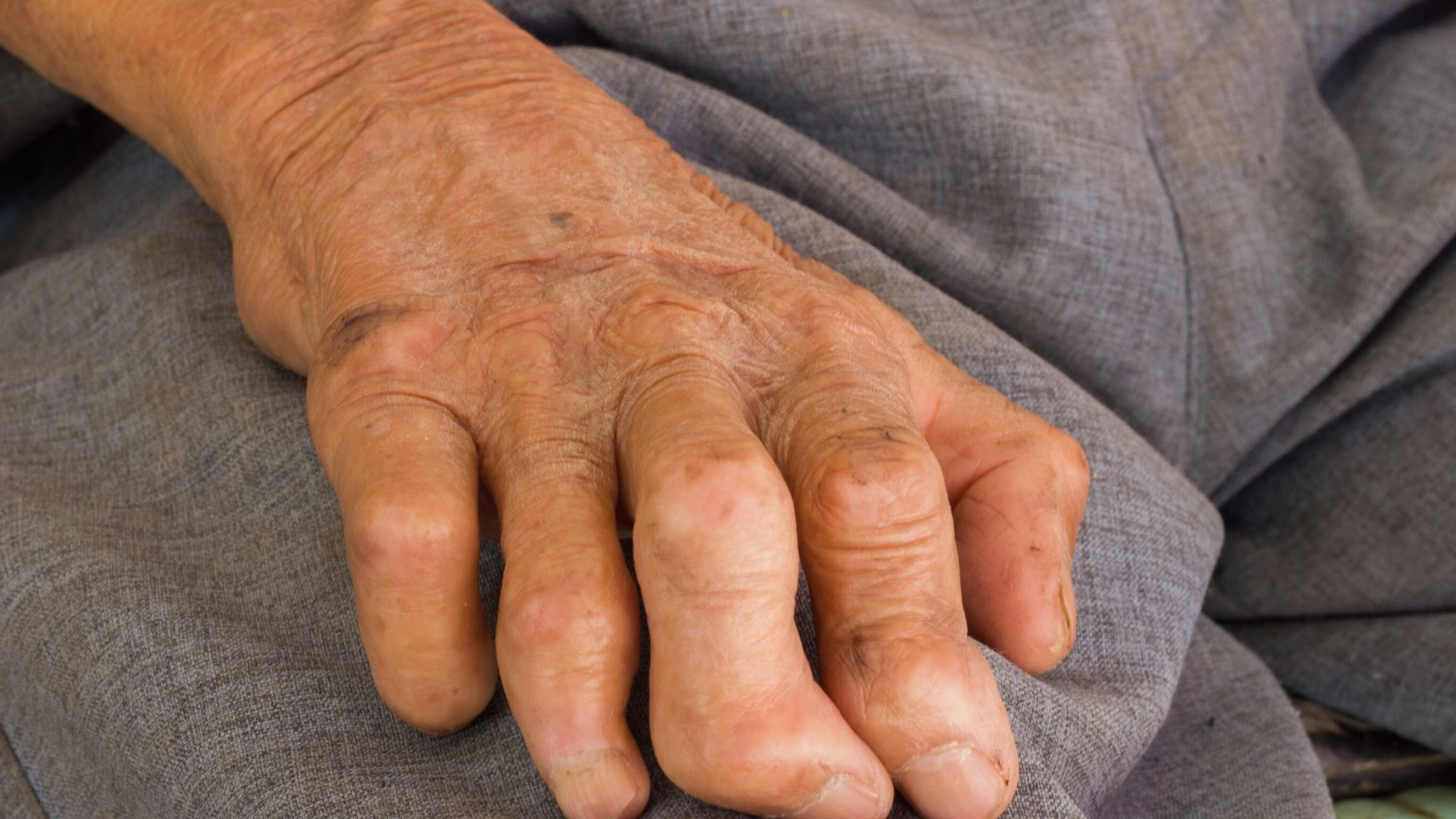
Leprosy, also known as Hansen’s disease, is an infectious condition caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae. This insidious pathogen primarily targets the skin and peripheral nervous system, leading to a range of symptoms that can result in disfigurement and nerve damage if left untreated. The understanding of its biological nature is not merely an academic exercise; it’s a vital foundation for grappling with the disease’s resurgence.
The manifestations of leprosy are diverse, ranging from mild skin lesions to severe neurological impairment. Early diagnosis is paramount, as timely intervention can prevent permanent disabilities. With modern medicine, leprosy is curable through a regimen of antibiotics, a fact that underscores the importance of awareness and early detection in both medical communities and the public at large.
Geographic Concentration: Focus On Florida

Florida’s emergence as the epicenter of leprosy cases in the U.S. warrants a detailed examination. Central Florida’s high concentration of cases raises questions about local factors that may be contributing to the spread, such as climate, population density, and interaction with specific animal species.
Compared to other states, Florida’s situation is unique. The state’s environment and demographics may offer insights into the disease’s transmission and control. This geographic focus sets the stage for a broader discussion on transmission patterns, including the connection between leprosy and armadillos.
Transmission: Travelers And Local Cases

Historically, leprosy cases in the U.S. were often linked to travelers entering the country. However, a shift has occurred in recent years, with approximately one-third of cases from 2015 to 2020 appearing to have been acquired locally. This change in transmission dynamics indicates that leprosy is no longer confined to isolated cases from abroad but has become a domestic public health concern.
The implications of this shift are profound, as it suggests a potential change in the epidemiology of the disease. Local transmission means that new strategies may be required for prevention and control. Understanding this shift is essential for adapting public health strategies to the local context, including potential animal reservoirs like armadillos.
The Armadillo Connection

Armadillos, known carriers of Mycobacterium leprae, have emerged as a potential source of infection in the U.S., particularly in Florida. This connection between armadillos and leprosy is not a new discovery, but the recent rise in cases has brought it back into focus. Understanding how armadillos contribute to the transmission of leprosy is a critical aspect of public health interventions, and it opens up new avenues for research and prevention.
The link between armadillos and leprosy adds a layer of complexity to the efforts to control the disease. It requires a multifaceted approach that includes medical treatment and public education about the risks of interacting with armadillos. This connection also raises questions about other potential animal carriers and how they might influence the spread of leprosy, a subject that warrants further investigation.
Public Health Response

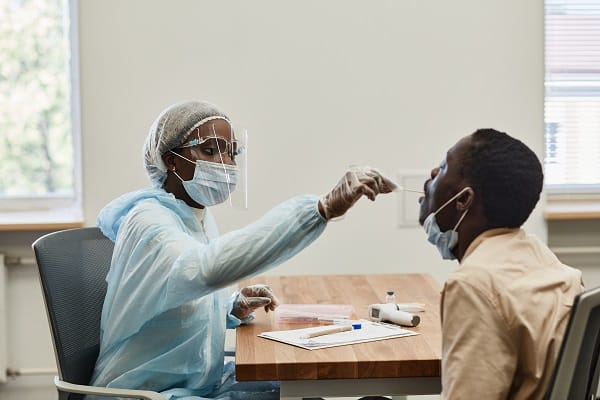
The increase in leprosy cases, particularly in Florida, has necessitated a robust and coordinated public health response. Government and health organizations have implemented measures such as increased surveillance and diagnostic testing. These efforts are not only aimed at identifying cases early but also at understanding the underlying factors contributing to the spread, such as local transmission and animal reservoirs.
Unfortunately, challenges in the public health response to leprosy are multifaceted, ranging from technical aspects like early diagnosis to social challenges like combating the lingering stigma associated with the disease. Continued vigilance, research, and compassionate care are essential components, but they must be integrated into a broader strategy considering the unique characteristics of the resurgence of leprosy. This approach sets the stage for a more comprehensive understanding of the disease and informs the development of targeted interventions.
The Global Perspective
Leprosy is a global issue, and the situation in the U.S. fits into a broader international context. While the U.S. has seen a gradual increase in cases, other countries have made significant strides in reducing the incidence of leprosy. Understanding the global perspective helps to contextualize the U.S. experience and informs international cooperation and efforts.
Comparing the U.S. situation with global trends offers insights into the unique challenges and opportunities in addressing leprosy. It emphasizes the importance of international collaboration, shared research, and best practices in combating this ancient disease. The global perspective also highlights the interconnectedness of public health, emphasizing the need for a unified approach to tackle leprosy and other infectious diseases.
Challenges And Concerns

The resurgence of leprosy in the U.S. is not just a matter of increased numbers; it presents unique obstacles that make it a particularly challenging public health issue. One of these challenges is the disease’s insidious nature, where symptoms may not appear for years, making early diagnosis difficult. This delay can lead to more severe outcomes, emphasizing the need for heightened awareness and screening.
Another distinct challenge is the multi-factorial transmission of the disease, involving not just human-to-human contact but also potential animal carriers like armadillos. This complexity necessitates a nuanced understanding of the disease’s ecology and a multifaceted approach to prevention and control. These unique obstacles require innovative solutions, collaboration across disciplines, and a willingness to explore uncharted territories in the fight against leprosy.
The Bottom Line
The resurgence of leprosy in the U.S., particularly in Florida, is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires a comprehensive and coordinated response. From understanding the causes and symptoms to addressing challenges and implementing prevention measures, the fight against leprosy is far from over. This post has explored the various aspects of this ancient disease’s modern resurgence, highlighting the importance of continued vigilance, research, and compassionate care. The lessons learned from this experience underscore the interconnection of public health and the need for a unified approach to tackle not only leprosy but all infectious diseases that continue to challenge society as a whole.